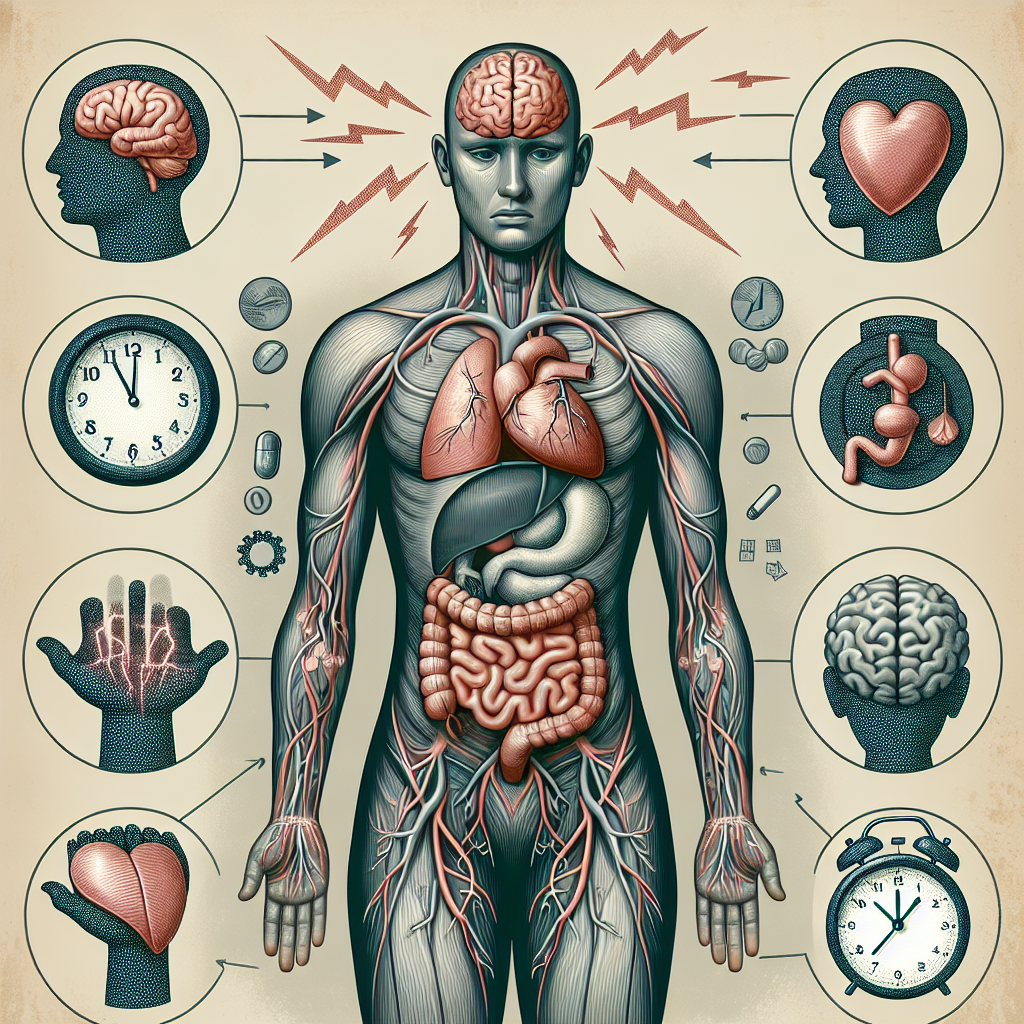
Stress is a common part of everyday life for many people, but its effects on the body are often underestimated. Stress can have a significant impact on both our mental and physical health, leading to a variety of negative consequences if left unchecked. Understanding how stress affects the body is essential for managing and reducing its impact on our overall well-being.
The body’s response to stress is known as the “fight or flight” response, a natural reaction that prepares us to either confront a threat or flee from it. When we perceive a potential stressor, whether it’s a tight deadline at work or a conflict with a loved one, our bodies release stress hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones trigger a series of physiological reactions that are designed to help us respond to the perceived threat.
One of the immediate effects of stress is an increase in heart rate and blood pressure, as the body gears up to face the perceived threat. This can lead to feelings of anxiety, tension, and unease. In the short term, these symptoms may not seem like a big deal, but over time, chronic stress can have a serious impact on our health.
Chronic stress is associated with a variety of health problems, including heart disease, high blood pressure, and diabetes. It can also weaken the immune system, making us more susceptible to illnesses. Research has shown that long-term stress can increase inflammation in the body, which is linked to a number of chronic conditions, including autoimmune diseases, arthritis, and even cancer.
Stress can also impact our mental health, leading to symptoms such as depression, anxiety, and insomnia. Chronic stress can interfere with our ability to concentrate, make decisions, and think clearly. It can also affect our relationships, leading to conflicts and strained connections with others.
In addition to its effects on physical and mental health, stress can also affect our behavior. People under stress may turn to unhealthy coping mechanisms such as overeating, smoking, or excessive drinking. These behaviors can further exacerbate the negative impact of stress on the body, leading to a cycle of poor health outcomes.
So, how does stress affect the body? In summary, stress triggers a series of physiological responses that can have both short-term and long-term effects on our health. Chronic stress can weaken the immune system, increase inflammation, and contribute to the development of chronic diseases. It can also impact our mental health and behavior, leading to a variety of negative consequences.
FAQs:
Q: How can I reduce stress in my life?
A: There are several ways to reduce stress, including exercise, meditation, deep breathing exercises, and spending time with loved ones. It’s also important to prioritize self-care and make time for activities that bring you joy and relaxation.
Q: Is stress always bad for you?
A: While some stress can be beneficial in helping us to respond to challenges, chronic stress can have serious negative effects on our health. It’s important to identify sources of stress in your life and take steps to manage them effectively.
Q: Can stress be managed through diet?
A: Eating a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help to support your body’s ability to cope with stress. Avoiding excessive caffeine, sugar, and processed foods can also help to reduce stress levels.
Q: When should I seek professional help for stress?
A: If you’re feeling overwhelmed by stress and it’s affecting your daily life, it may be time to seek professional help. A therapist or counselor can provide support and guidance in developing strategies to manage stress effectively.