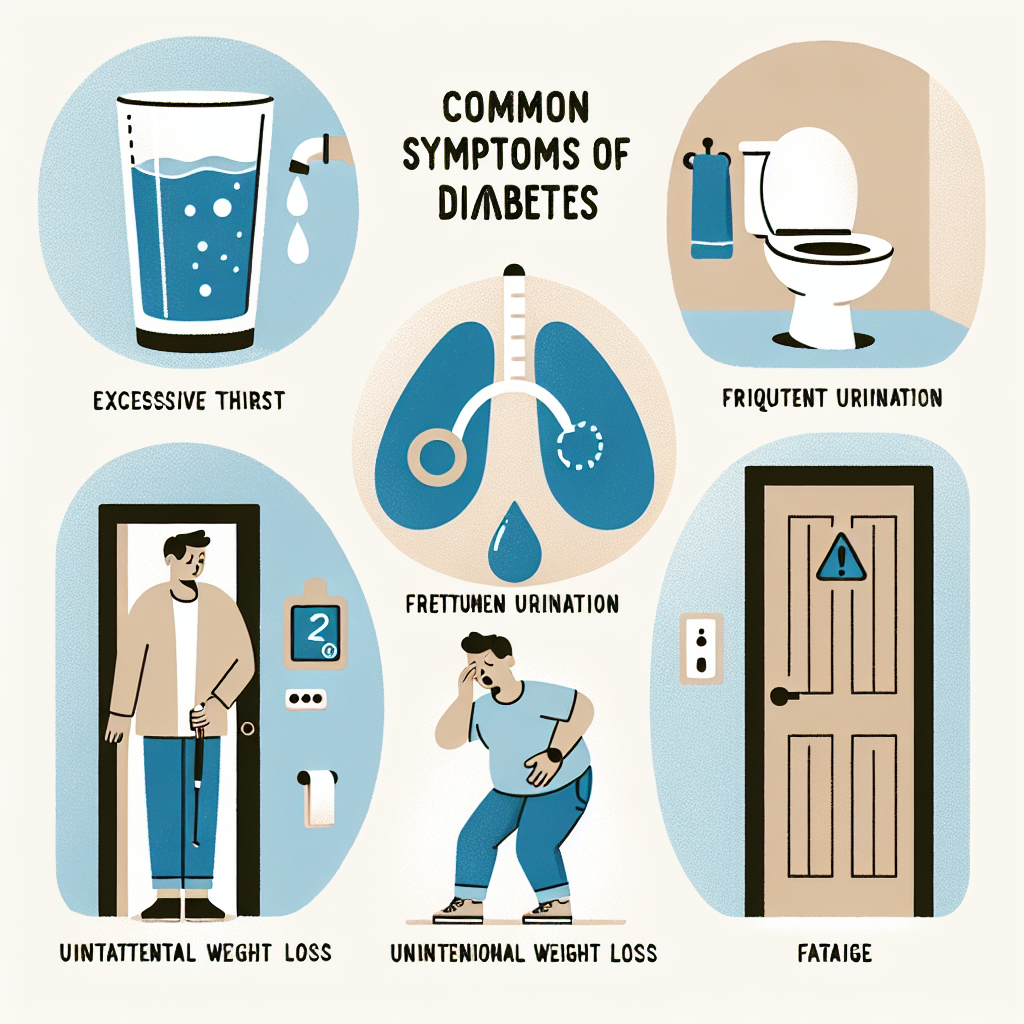
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the body is unable to properly regulate blood sugar levels, leading to high levels of glucose in the blood. This can have serious consequences if left untreated, including damage to the heart, kidneys, eyes, and nerves. Knowing the common symptoms of diabetes is crucial for early detection and management of the condition.
Common Symptoms of Diabetes:
1. Frequent urination: One of the most common symptoms of diabetes is frequent urination. This is due to the high levels of glucose in the blood, which causes the kidneys to work overtime to eliminate the excess sugar through urine.
2. Increased thirst: Increased urination can lead to dehydration, causing the body to signal thirst as a way to try to replenish lost fluids.
3. Unexplained weight loss: Despite increased appetite, people with diabetes may experience weight loss due to the body’s inability to properly use glucose for energy.
4. Fatigue: High levels of glucose in the blood can prevent cells from getting the energy they need, leading to feelings of fatigue and tiredness.
5. Blurred vision: Diabetes can cause changes in the fluid levels of the eye, leading to blurry vision.
6. Slow healing of wounds: High levels of glucose can impair the body’s ability to heal itself, leading to slow wound healing.
7. Tingling or numbness in the hands or feet: Diabetes can cause damage to nerves, leading to a tingling sensation or numbness in the extremities.
8. Recurring infections: High levels of glucose in the blood can weaken the immune system, making people with diabetes more susceptible to infections.
9. Darkened skin patches: Diabetes can cause changes in the skin’s pigmentation, leading to darkened patches on the neck or armpits.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to speak with your healthcare provider for further evaluation and testing. Early detection and management of diabetes can help prevent complications and improve quality of life.
FAQs:
Q: Can diabetes be cured?
A: There is currently no cure for diabetes, but it can be managed through lifestyle changes, medication, and regular monitoring of blood sugar levels.
Q: What are the risk factors for diabetes?
A: Risk factors for diabetes include family history, obesity, poor diet, physical inactivity, and age.
Q: How is diabetes diagnosed?
A: Diabetes is diagnosed through blood tests that measure blood sugar levels. A fasting blood sugar test, oral glucose tolerance test, or A1c test may be used for diagnosis.
Q: What are the complications of diabetes?
A: Complications of diabetes include heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, eye problems, and foot problems.
Q: How can diabetes be managed?
A: Diabetes can be managed through diet and exercise, monitoring blood sugar levels, taking medication as prescribed, and regular check-ups with a healthcare provider.
In conclusion, knowing the common symptoms of diabetes is crucial for early detection and management of the condition. If you are experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned above, it is important to speak with your healthcare provider for further evaluation and testing. With proper management, people with diabetes can lead healthy and fulfilling lives.