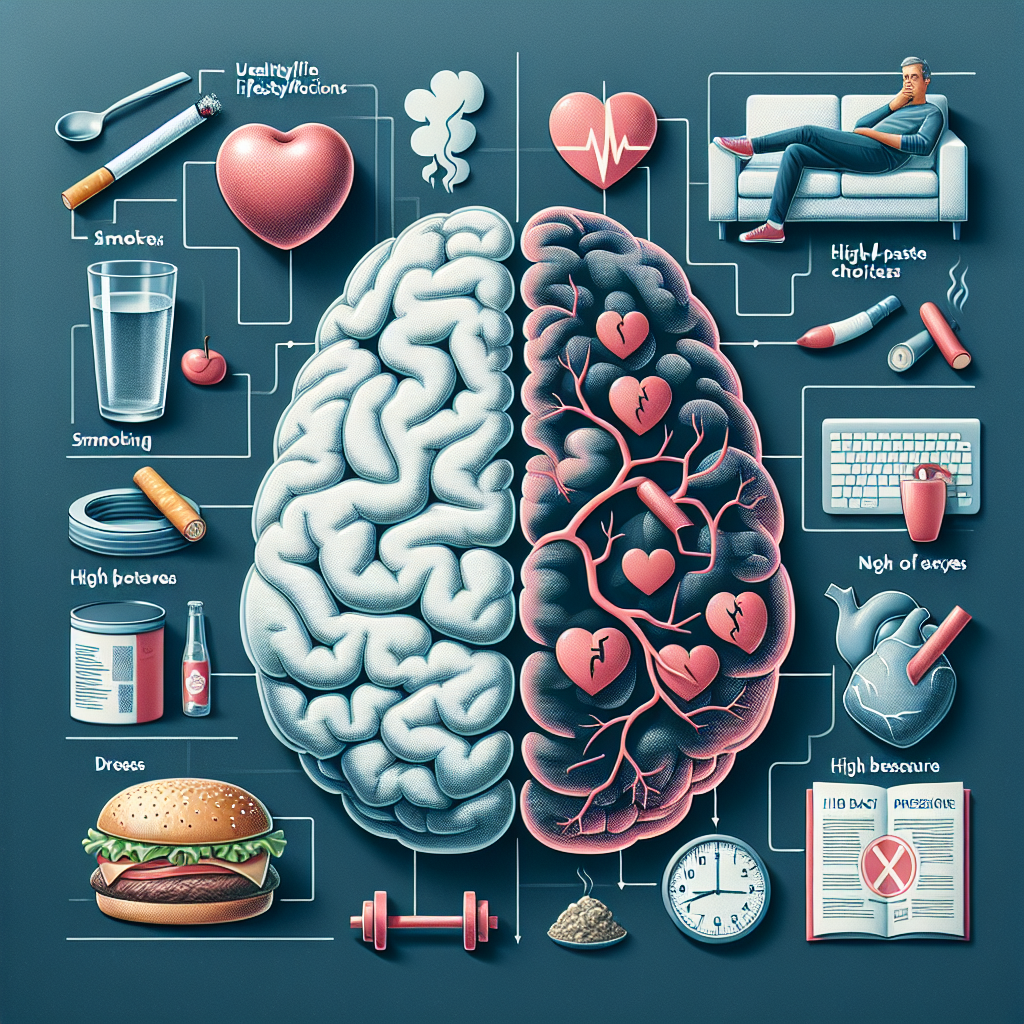
Stroke is a serious medical condition that occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain is disrupted, either by a blockage in a blood vessel or by bleeding in the brain. This interruption in blood flow deprives the brain of oxygen and nutrients, leading to damage or cell death within minutes. A stroke can have devastating consequences, including paralysis, speech difficulties, and even death. Understanding the common causes of stroke is crucial in order to reduce the risk of experiencing this life-threatening event.
There are several factors that can increase the risk of stroke. Some of the common causes of stroke include:
1. High blood pressure: High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a major risk factor for stroke. When blood pressure is consistently high, it can damage the walls of blood vessels, making them more susceptible to blockages or rupture. Controlling high blood pressure through lifestyle changes and medication can significantly reduce the risk of stroke.
2. Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for stroke. The chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of blood clots, leading to blockages in the arteries that supply blood to the brain. Quitting smoking is one of the most effective ways to lower the risk of stroke.
3. Diabetes: People with diabetes are at a higher risk of stroke because high blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of clot formation. Managing diabetes through diet, exercise, and medication can help reduce the risk of stroke.
4. High cholesterol: High levels of cholesterol in the blood can lead to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, narrowing the passageways through which blood flows. This can increase the risk of blockages and reduce blood flow to the brain, increasing the risk of stroke. Lowering cholesterol levels through diet, exercise, and medication can help reduce the risk of stroke.
5. Obesity: Being overweight or obese increases the risk of stroke because excess body fat can lead to higher blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol levels. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can help reduce the risk of stroke.
6. Physical inactivity: Lack of exercise can increase the risk of stroke by contributing to other risk factors, such as obesity, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol. Regular physical activity can help lower blood pressure, improve cholesterol levels, and maintain a healthy weight, reducing the risk of stroke.
7. Family history: A family history of stroke or heart disease can increase the risk of stroke. Genetics can play a role in predisposing individuals to conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol, all of which are risk factors for stroke. Knowing your family history can help you understand your risk and take preventive measures.
8. Age: The risk of stroke increases with age, with the majority of strokes occurring in people over the age of 65. As people age, blood vessels can become less flexible and more prone to damage, increasing the risk of blockages or rupture. However, strokes can also occur in younger people, particularly those with other risk factors.
9. Gender: Men are at a higher risk of stroke than women, but women are more likely to die from a stroke. Hormonal changes, pregnancy, and birth control pills can all affect a woman’s risk of stroke. Women should be aware of these risk factors and take appropriate steps to reduce their risk.
10. Other medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as atrial fibrillation, heart disease, and sickle cell disease, can increase the risk of stroke. Atrial fibrillation, in particular, is a type of irregular heartbeat that can lead to the formation of blood clots in the heart, which can travel to the brain and cause a stroke.
In addition to these common causes, there are other factors that can increase the risk of stroke, such as excessive alcohol consumption, drug abuse, and sleep apnea. It is important to be aware of these risk factors and take steps to reduce your risk of stroke.
FAQs about stroke:
Q: What are the warning signs of a stroke?
A: The most common warning signs of a stroke are sudden numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body; sudden confusion, trouble speaking or understanding speech; sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes; sudden trouble walking, dizziness, loss of balance or coordination; and sudden severe headache with no known cause.
Q: What should I do if I suspect someone is having a stroke?
A: If you suspect someone is having a stroke, it is important to act quickly. Call emergency services immediately and note the time when the symptoms first appeared. Do not wait for the symptoms to go away, as time is of the essence in treating a stroke. Stay with the person and keep them calm while waiting for help to arrive.
Q: How is a stroke diagnosed and treated?
A: A stroke is typically diagnosed through a physical exam, imaging tests such as a CT scan or MRI, and blood tests. Treatment for a stroke may include medication to dissolve blood clots, surgery to remove blockages, or rehabilitation to help patients regain lost abilities.
Q: Can stroke be prevented?
A: While not all strokes can be prevented, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk. These include controlling high blood pressure, quitting smoking, managing diabetes, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and limiting alcohol consumption. It is also important to be aware of your family history and seek medical attention for any symptoms of stroke.
In conclusion, understanding the common causes of stroke is essential for reducing the risk of experiencing this life-threatening event. By being aware of risk factors such as high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, and obesity, and taking steps to address them, you can lower your risk of stroke and improve your overall health. If you have any concerns about your risk of stroke or are experiencing symptoms of a stroke, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Remember, time is of the essence in treating a stroke, so act quickly to protect your health and wellbeing.